IRS Announces IRA and Retirement Plan Limits for 2016

Many IRA and retirement plan limits are indexed for inflation each year. On October 21, 2015, the IRS (in IR-2015-118) issued the inflation-adjusted numbers for 2016, and most remain unchanged from 2015. We’ve summarized the announcement here:
IRA contribution limits
The maximum amount you can contribute to a traditional IRA or Roth IRA in 2016 is $5,500 (or 100% of your earned income, if less), unchanged from 2015. The maximum catch-up contribution for those age 50 or older remains at $1,000. (You can contribute to both a traditional and Roth IRA in 2016, but your total contributions can’t exceed these annual limits.)
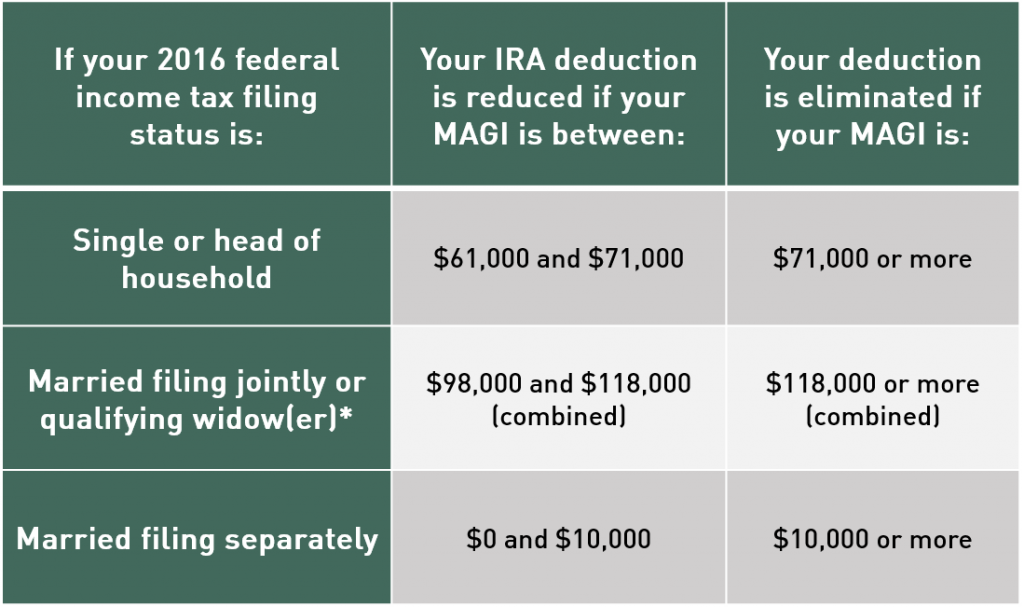
Traditional IRA deduction limits for 2016
The income limits for determining the deductibility of traditional IRA contributions in 2016 are unchanged, except for one instance: if you’re not covered by an employer plan but your spouse is, and you file a joint return, you can fully deduct your IRA contribution in 2016 if your MAGI (Modified Adjusted Gross Income) is $184,000 or less (up from $183,000 in 2015).
*If you’re not covered by an employer plan but your spouse is, your deduction is limited if your MAGI is $184,000 to $194,000, and eliminated if your MAGI exceeds $194,000.
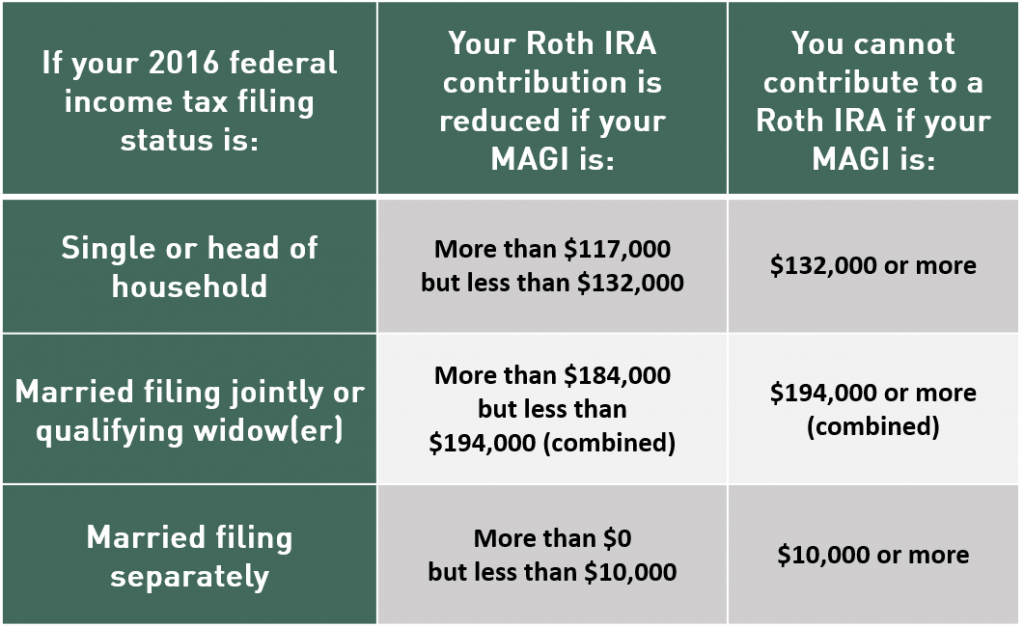
Roth IRA contribution limits for 2016
The income limits for determining how much you can contribute to a Roth IRA have increased for 2016. If your filing status is single or head of household, you can contribute the full $5,500 to a Roth IRA in 2016 if your MAGI is $117,000 or less (up from $116,000 in 2015). And if you’re married and filing a joint return, you can make a full contribution in 2016 if your MAGI is $184,000 or less (up from $183,000 in 2015). (Again, contributions
can’t exceed 100% of your earned income.)
Employer retirement plans
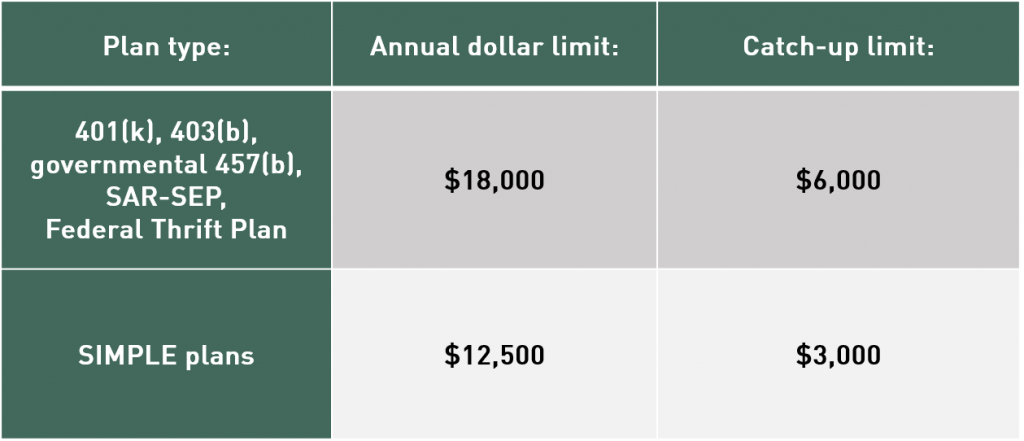
All of the significant employer retirement plan limits for 2016 remain unchanged from 2015. The maximum amount you can contribute (your “elective deferrals”) to a 401(k) plan in 2016 is $18,000. This limit also applies to 403(b), 457(b), and SAR-SEP plans, as well as the Federal Thrift Plan. If you’re age 50 or older, you can also make catch-up contributions of up to $6,000 to these plans in 2016. (Special catch-up limits apply to certain participants
in 403(b) and 457(b) plans.)
If you participate in more than one retirement plan, your total elective deferrals can’t exceed the annual limit ($18,000 in 2016 plus any applicable catch-up contribution). Deferrals to 401(k) plans, 403(b) plans, SIMPLE plans, and SAR-SEPs are included in this aggregate limit, but deferrals to Section 457(b) plans are not. For example, if you participate in both a 403(b) plan and a 457(b) plan, you can defer the full dollar limit to each plan–a total of $36,000 in 2016 (plus any catch-up contributions).
The amount you can contribute to a SIMPLE IRA or SIMPLE 401(k) plan in 2016 is $12,500, and the catch-up limit for those age 50 or older remains at $3,000.
Note: Contributions can’t exceed 100% of your income.
The maximum amount that can be allocated to your account in a defined contribution plan (for example, a 401(k) plan or profit-sharing plan) in 2016 is $53,000, plus age-50 catch-up
contributions. (This includes both your contributions and your employer’s contributions. Special rules apply if your employer sponsors more than one retirement plan.)
Finally, the maximum amount of compensation that can be taken into account in determining benefits for most plans in 2016 is $265,000, and the dollar threshold for determining highly compensated employees (when 2016 is the look-back year) is $120,000, both unchanged from 2015.
IMPORTANT DISCLOSURES
Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc. does not provide investment, tax, or legal advice. The information presented here is not specific to any individual’s personal circumstances.
To the extent that this material concerns tax matters, it is not intended or written to be used, and cannot be used, by a taxpayer for the purpose of avoiding penalties that may be imposed by law. Each taxpayer should seek independent advice from a tax professional based on his or her individual circumstances.
These materials are provided for general information and educational purposes based upon publicly available information from sources believed to be reliable—we cannot assure the accuracy or completeness of these materials. The information in these materials may change at any time and without notice.